Understanding the risk management process is crucial for both cybersecurity professionals and students gearing up for cybersecurity exams. Today, danger lurks everywhere in digital spaces. Companies can’t just react after something bad happens. They need a well-planned strategy. Risk management gives a solid plan to protect important systems & data. For budding cybersecurity experts, getting good at this means being ready to spot, check out, and fix problems before they get worse. It changes unknown threats into manageable situations that match security plans with company goals & rules.
So, here comes the risk management process—a thoughtful way to spot, check, and lessen possible threats to what an organization wants to do. By getting a good risk management plan in place, businesses can guard themselves from harm and gain a competitive edge in their industries. By the end of this post, you’ll have a complete grasp of how to deal with the tricky world of organizational risks and come out tougher and more ready.
Table of Contents
Defining Risk Management in Cybersecurity
As we explore the complexities of risk management, we’ll consider important aspects such as defining the concept, spotting possible risks, checking and ranking threats, planning response strategies, implementing control measures, monitoring progress, and sharing risk management efforts.
Risk management is a smart way to spot and rate risks to keep a business running. You have to check out which problems might pop up, how likely they are, and what damage they could do. In cybersecurity, it’s the guiding star for security decisions. Like checking the weather before a road trip, teams predict risks to be ready and cut down on trouble. With this plan, companies link up cybersecurity costs with big risks.
Analogies and Examples
Think about risk management like planning a big trip across the country. You look at weather updates, pack just in case (emergencies), and plan backup routes. Doing this reduces surprises & makes the trip smoother. For businesses, this means preparing systems for cyber threats ahead of time. For example, a finance company sees cyber threats as risky & uses encryption & regular checks. Meanwhile, a factory might focus less on data loss and more on maintenance.
Key Parts of the Risk Management Process
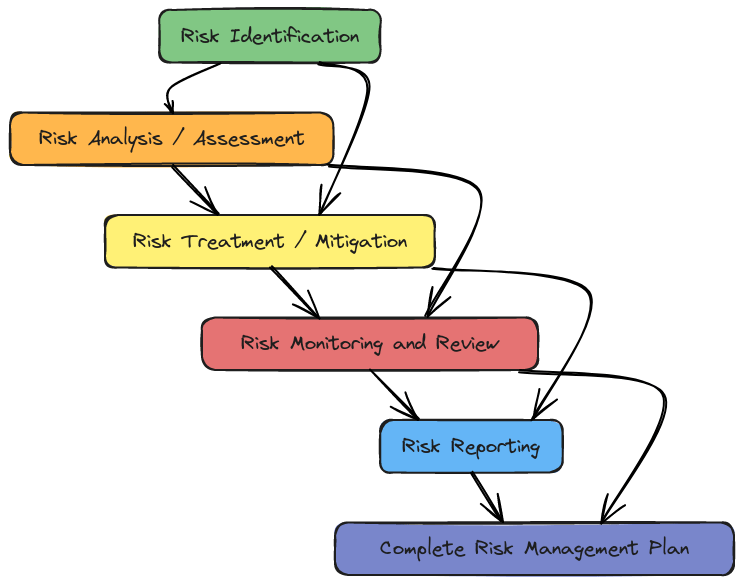
The risk management process has several key pieces working together to make a full plan. These pieces include:
- Risk Identification
- Risk Analysis/Assessment
- Risk Treatment/Mitigation
- Risk Monitoring and Review
- Risk Reporting
Each piece is crucial in the whole risk management process. Let’s dive deeper into each one:
| Component | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Identification | Recognizing potential threats and vulnerabilities | Forms the foundation of risk management |
| Risk Analysis/Assessment | Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks | Helps prioritize risks and allocate resources |
| Risk Treatment/Mitigation | Developing strategies to reduce or eliminate risks | Minimizes potential negative impacts |
| Risk Monitoring and Review | Continuously tracking and reviewing risk factors | Ensures ongoing effectiveness of risk management |
| Risk Reporting | Communicating risk-related information to stakeholders | Promotes transparency and informed decision-making |
Benefits of Good Risk Management
Having a good risk management process gives organizations lots of perks:
- Better decision-making
- Stronger organizational resilience
- More trust with stakeholders
- Smarter resource use
- Fewer money losses
- Meets rules and standards
Common Myths About Risk Management
Even with its importance, risk management is often misunderstood. Some myths are:
- It’s just about avoiding risks.
- It’s a one-time thing.
- It’s only for the risk management department.
- All risks can be wiped out.
- It’s too pricey and time-consuming.
Getting these wrong notions straight is key to putting a strong risk management plan in place. By clearing up these myths, organizations can build a more positive & realistic way to handle risks.
5 Parts of the Risk Management Process
1. Risk Identification
Start by listing potential threats. Companies use tools like brainstorming, expert talks, and looking back at past issues. SWOT analysis finds insider weaknesses & outside threats. The aim? Cover everything that could go wrong—from email scams to natural disasters—so no potential danger gets missed.
Brainstorming techniques for risk identification
Good risk spotting starts with team brainstorming. Sessions should include different team members to get a wide range of views. Some popular techniques are
- Mind mapping
- SWOT analysis
- Cause-and-effect diagrams
- The 5 Whys method
| Technique | Description | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Mind mapping | Visual brainstorming tool | Complex, interconnected risks |
| SWOT analysis | Identifies Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats | Strategic risk assessment |
| Cause-and-effect diagrams | Visualizes potential causes of risks | Root cause analysis |
| The 5 Whys | Repeatedly asks “why” to uncover root causes | Detailed risk exploration |
Analyzing historical data and trends
Historical data provides valuable insights into potential future risks. Key steps include:
- Collecting relevant data from past projects or similar industries
- Identifying patterns and trends
- Extrapolating potential future risks based on observed patterns
Utilizing risk assessment tools
Various tools can streamline the risk identification process:
- Risk registers
- Risk breakdown structures
- Probability and impact matrices
- Scenario analysis software
Conducting stakeholder interviews
Engaging stakeholders is crucial for comprehensive risk identification. Consider:
- Preparing targeted questions
- Conducting one-on-one interviews or focus groups
- Encouraging open and honest communication
- Documenting and analyzing stakeholder input
By employing these methods, organizations can create a robust foundation for their risk management strategy. The next step involves assessing and prioritizing the identified risks to determine which require immediate attention and resources.
2. Risk Analysis/Assessment
After listing risks, they need to be checked out in terms of chance & impact. This stage can be simple, like using “low” or “high,” or more detailed, using numbers like annualized loss expectancy (ALE) to know which risks need a quick fix. The risk assessment process helps to prioritize the risks.
Prioritizing risks lets security teams zero in on those that might shake things up the most. Like cyberattacks on money data. These are often first on the list because they can harm reputation and break rules. Meanwhile, smaller software mess-ups might not matter as much. A solid risk management process saves time and resources for the biggest threats. For example, ransomware that happens often & costs lots of money takes priority over rare, minor ones.
Qualitative risk analysis techniques
Qualitative risk analysis involves assessing risks based on their potential impact and likelihood using subjective methods. Common techniques include:
- Expert judgment
- Risk probability and impact assessment
- Risk categorization
These methods help organizations quickly identify and prioritize risks without extensive numerical data.
Quantitative risk analysis techniques
Quantitative analysis uses numerical data to evaluate risks more precisely. Key techniques include:
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Decision tree analysis
- Expected Monetary Value (EMV) analysis
| Technique | Description | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Monte Carlo | Uses probability distributions to simulate outcomes | Provides range of possible results |
| Decision tree | Maps out potential decisions and outcomes | Helps visualize complex scenarios |
| EMV | Calculates average outcome considering probabilities | Useful for comparing alternatives |
Creating a risk matrix
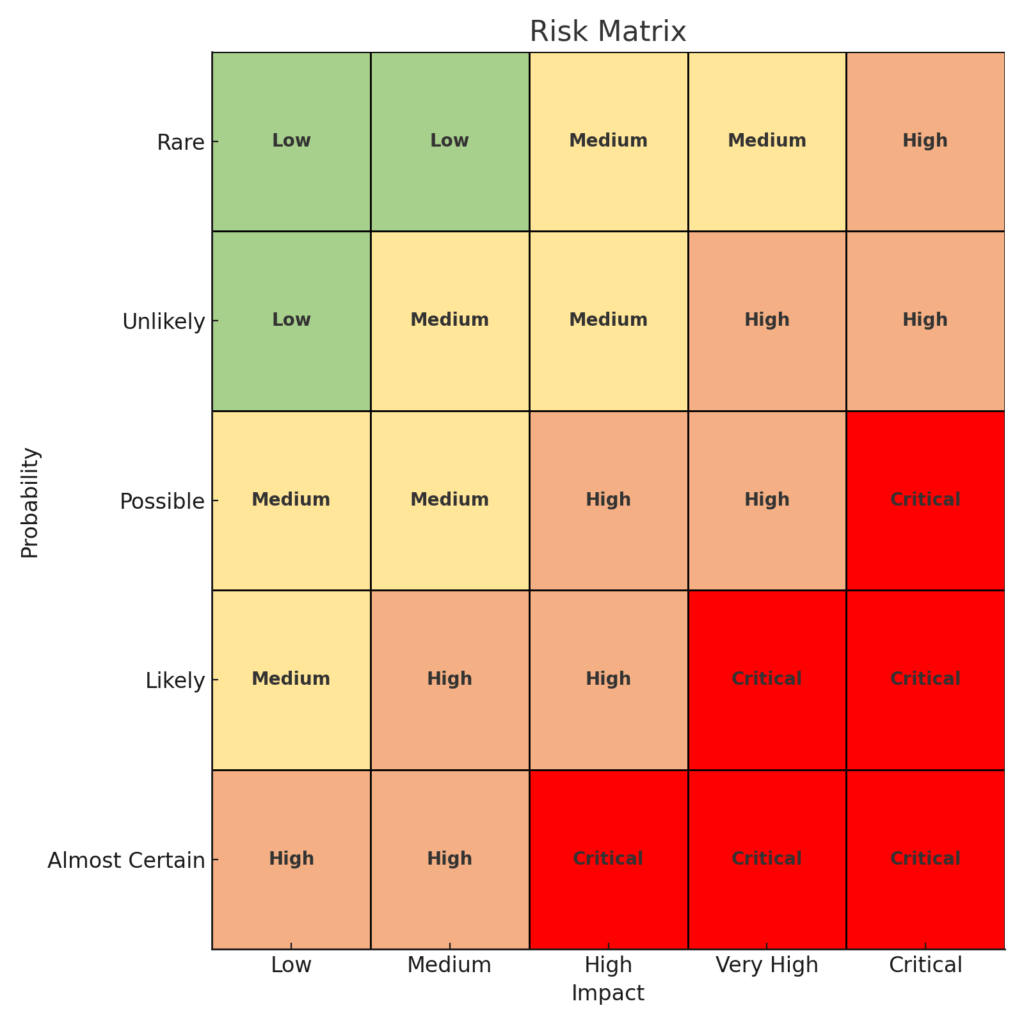
A risk matrix is a visual tool that combines impact and probability assessments. Steps to create one:
- Define impact and probability scales
- Plot risks on the matrix
- Assign color codes (e.g., red for high-risk, green for low-risk)
- Use the matrix to prioritize risks
Determining risk tolerance levels
Risk tolerance defines the level of risk an organization is willing to accept. Factors influencing tolerance:
- Organizational culture
- Industry standards
- Regulatory requirements
- Stakeholder expectations
Prioritizing risks based on impact and probability
Once risks are assessed, they can be prioritized using:
- Risk scores (impact × probability)
- Risk categories (high, medium, low)
- Alignment with organizational objectives
This prioritization helps focus resources on the most critical risks. With a clear understanding of risk assessment and prioritization, organizations can develop effective risk response strategies.
3. Risk Treatment/Mitigation
With prioritized risks, businesses pick how to deal with them. Treatment falls into four buckets. Mitigation cuts back on risk, like through stronger security walls. Transfer passes risk to someone else, like insurance companies do. Acceptance means recognizing a small risk but deciding not to act on it. Avoidance stops risk by ending the causing activity.
Risk avoidance techniques
Risk avoidance is the most straightforward strategy in risk management. It involves eliminating the possibility of a risk occurring by avoiding the activity or situation that could lead to it. Here are some common risk-avoidance techniques:
- Discontinuing high-risk products or services
- Exiting volatile markets
- Rejecting risky business partnerships
- Implementing strict safety protocols
Risk mitigation strategies
When risks cannot be entirely avoided, mitigation strategies come into play. These strategies aim to reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk. Consider the following approaches:
- Diversification of investments or operations
- Implementation of safety measures and backup systems
- Staff training and skill development
- Regular maintenance and quality control
| Strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Diversification | Spreading risk across multiple areas | Investing in various industries |
| Safety Measures | Implementing protective systems | Installing fire alarms |
| Training | Enhancing staff capabilities | Cybersecurity awareness programs |
| Maintenance | Regular upkeep to prevent issues | Scheduled equipment checks |
Risk transfer options
Risk transfer involves shifting the potential impact of a risk to another party. This can be achieved through:
- Insurance policies
- Outsourcing risky activities
- Contractual agreements with suppliers or partners
Risk acceptance considerations
Sometimes, accepting a risk is the most appropriate strategy, especially when the cost of other responses outweighs the potential impact. Factors to consider include:
- Cost-benefit analysis of risk response options
- The organization’s risk tolerance level
- Potential opportunities associated with the risk
Now that we’ve explored various risk response strategies, let’s look at how to implement these through effective risk control measures.
Real-World Illustrations
Take an IT company spotting phishing attacks rising. After checking their frequency & effect, it puts email filters & staff practice sessions into action. That’s mitigation for you! Meanwhile, a shop chain in flood areas buys business halt insurance to transfer risk.
Implementing Risk Control Measures
Assigning risk ownership
Risk ownership is a crucial step in implementing effective risk control measures. It involves designating specific individuals or teams responsible for managing and mitigating identified risks. Here’s a breakdown of key aspects:
- Clear accountability
- Decision-making authority
- Resource allocation
- Regular reporting
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Risk Owner | Overall accountability for risk management |
| Risk Manager | Day-to-day risk monitoring and control |
| Executive Sponsor | Strategic oversight and resource approval |
Establishing key risk indicators (KRIs)
KRIs are measurable metrics that provide early warnings of potential risks. They help organizations proactively identify and address emerging threats. Consider the following when establishing KRIs:
- Align with organizational objectives
- Ensure measurability and relevance
- Set appropriate thresholds
- Regular review and update
Developing contingency plans
Contingency plans outline specific actions to be taken in the event of risk materialization. These plans should be:
- Comprehensive
- Easily accessible
- Regularly updated
- Tested through simulations
Creating risk management policies and procedures
Effective risk management requires well-defined policies and procedures. These documents should:
- Clearly outline roles and responsibilities
- Establish risk assessment methodologies
- Define reporting and escalation protocols
- Incorporate regulatory requirements
By implementing these risk control measures, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to manage and mitigate potential threats. The next step involves ongoing monitoring and review of risks to ensure the effectiveness of these measures.
4. Risk Monitoring and Review

Risks change with new technology and rules. So, managing risks doesn’t stop after finding and fixing them. Ongoing checks ensure a business stays aware of new threats, and current fixes keep working. Regular checks, audits, and real-time tracking help stay on top of things. By keeping up-to-date with risks, businesses stay strong even as cyber threats keep changing.
Continuous risk assessment practices
Effective risk management requires ongoing vigilance. Continuous risk assessment practices involve:
- Regular risk reviews
- Real-time monitoring of key risk indicators
- Periodic reassessment of risk appetite
Implementing these practices ensures that your organization stays ahead of potential threats and opportunities.
| Practice | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Risk reviews | Monthly | Identifies new risks |
| KRI monitoring | Daily | Provides early warning |
| Risk appetite reassessment | Quarterly | Aligns with strategy |
Updating risk registers
A risk register is a living document that should be updated regularly. Key steps include:
- Adding newly identified risks
- Updating risk ratings and priorities
- Documenting changes in risk mitigation strategies
- Removing obsolete risks
Conducting regular risk audits
Risk audits provide an objective assessment of your risk management processes. They should:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of current risk controls
- Identify gaps in risk management practices
- Recommend improvements to strengthen risk management
Adapting to changing risk landscapes
As business environments evolve, so do risks. To stay resilient:
- Monitor industry trends and emerging risks
- Conduct scenario analysis for potential future risks
- Adjust risk management strategies accordingly
By maintaining a dynamic approach to risk monitoring and review, organizations can better navigate uncertainties and capitalize on opportunities. This proactive stance sets the stage for effective risk communication, which we’ll explore in the next section.
5. Risk reporting
Developing a risk communication plan
A robust risk communication plan is essential for effective risk management. Consider the following elements when developing your plan:
- Identify key stakeholders
- Determine communication channels
- Create clear messaging
- Establish communication frequency
- Assign responsibilities
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Stakeholders | Board members, executives, employees, customers, suppliers |
| Channels | Email, meetings, reports, intranet, social media |
| Messaging | Clear, concise, and tailored to each stakeholder group |
| Frequency | Regular updates, ad-hoc for urgent matters |
| Responsibilities | Assign team members to specific communication tasks |
Reporting to stakeholders
Effective stakeholder reporting ensures transparency and builds trust. Key aspects include:
- Regular updates on risk status
- Clear presentation of risk mitigation efforts
- Highlighting emerging risks and opportunities
- Providing context for risk-related decisions
Training employees on risk management
Employee training is crucial for successful risk management implementation:
- Conduct regular risk management workshops
- Provide online training modules
- Offer role-specific risk management guidance
- Encourage participation in risk identification and mitigation
Fostering a risk-aware organizational culture
Building a risk-aware culture involves:
- Leadership commitment to risk management
- Integrating risk considerations into decision-making processes
- Encouraging open communication about risks
- Recognizing and rewarding proactive risk management efforts
By effectively communicating risk management efforts, organizations can ensure that all stakeholders are aligned and actively contribute to the risk management process. This comprehensive approach helps in creating a more resilient and adaptive organization.
Conclusion
Effective risk management is a critical component of any successful organization. By following a structured process that includes identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, developing response strategies, and implementing control measures, businesses can better protect themselves from unforeseen challenges. Regular monitoring and review of risks, coupled with clear communication of risk management efforts, ensure that the organization remains resilient and adaptable in the face of changing circumstances.
Ultimately, understanding and implementing a comprehensive risk management process is not just about avoiding potential pitfalls; it’s about creating a culture of proactive decision-making and continuous improvement. By embracing risk management as an integral part of your business strategy, you can turn potential threats into opportunities for growth and innovation, positioning your organization for long-term success in an ever-evolving business landscape.
FAQs for Risk Management Process in Cybersecurity
Why is the risk management process important in cybersecurity?
It helps find and deal with risks, minimizing disruptions and breaches in business.
How often should a risk management process be reviewed?
At least every three months or when big changes happen in operations or threats.
Which treatment strategy is most common?
Mitigation is most prevalent, involving proactive controls like encryption and network segmentation.
How does risk assessment fit in?
It ranks threats based on possibility & impact, guiding the next steps in handling them.
Why are exams focused on the risk management process?
Because it reflects real-world practices & is key to good governance and compliance in cybersecurity.









